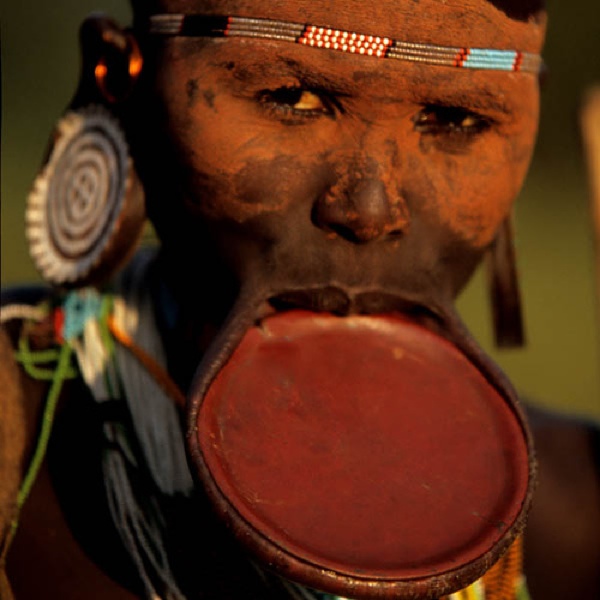
The Surma tribe of Ethiopia avoided all Western contact for years. Though they were well-known by Westerners for their giant lip plugs, they wanted nothing to do with any sort of government. The Surma lived in groups of a few hundred, and carried on with their humble cattle ranching for centuries while colonization, World Wars, and struggles for independence were going on all around them. The first people to hold a conversation with the Surma people were a few Russian doctors in the 1980s, thought by the tribesmen to be walking dead because of their skin color. One of the few fixtures of modernity adopted by the Surma is the use of AK-47s to protect their livestock.
While marching through the jungles of Peru, a tour group suddenly found itself face to face with the members of an unknown tribe. Everything was captured on film: the tribe tried to communicate with the tourists—but since the tribesmen didn’t know either Spanish or English, they soon gave up and left the bewildered moderns where they’d found them. Peruvian authorities, when they inspected the footage, soon realized that the tour group had stumbled upon one of the few remaining tribes unknown to anthropologists. Scientists had known about their existence and had been searching for them for years without success; the tourists found them without even trying.
During the 1700s, European settlers wrapped up their colonization of North America’s East Coast. By this point, every tribe between the Atlantic Ocean and the Mississippi River had been added to the catalogue of known peoples. Every tribe except for one, that is. In the 1790s, a previously unheard-of tribe of Native Americans walked out of the woods just thirty-five miles (56 km) from New York City. Somehow they had managed to avoid all contact with the settlers, despite some of the largest battles of both the Seven Years’ War and the Revolutionary War being waged in their backyard. They became known as the Jackson Whites, as they had a light skin color and were thought to have been descended from “Jacks” (slang for the British).
The Vietnam War brought unprecedented bombing to previously isolated regions. After one particularly enormous American bombing raid, the North Vietnamese soldiers were shocked to see a group of tribesmen emerge from the jungle. This was the Ruc tribe’s first contact with technologically advanced people. Due to the jungle damage, the Ruc decided to stay on in modern Vietnam rather than return to their traditional homes. But the tribal values picked up over hundreds of years soon clashed with the communist Vietnamese government, leading to mutual animosity.
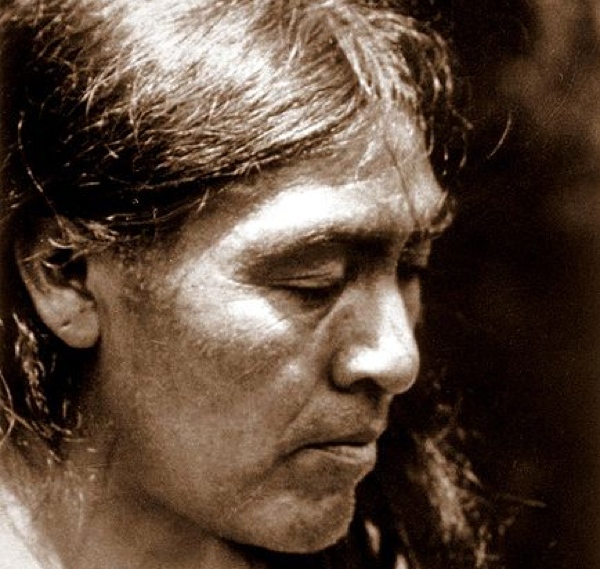
In 1911, the last Native American undisturbed by settlers calmly walked out of the forests in California, in full tribal dress—only to be arrested by stunned police. His name was Ishi, and he was a member of the Yahia tribe. After being questioned by police, who had found an interpreter from the local college, it was learned that Ishi was the sole survivor of a raid by settlers three years earlier. After struggling since then to live off the land by himself, he finally decided to contact other people for help. Ishi was taken by a researcher to Berkeley University, where he told the academic staff the secrets of his native life, and showed them many techniques for living off the land that had been long forgotten, or at least unknown to researchers.
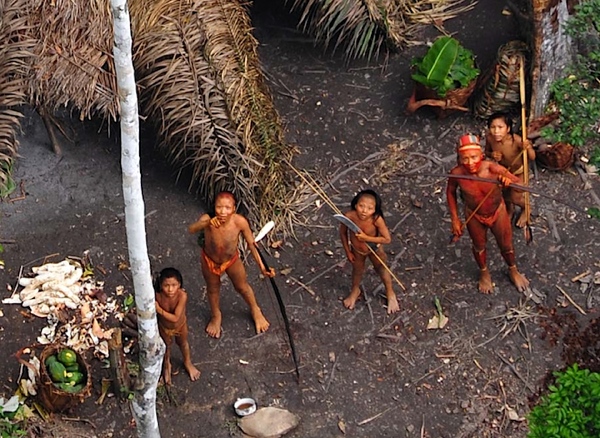
In 2007, a routine low-flying photo operation suddenly came under fire by arrows shot from the bows of a previously unknown tribe. And then in 2011, a satellite sweep managed to find a few specks in a corner of the jungle no one thought was habitable: it turns out that the specks were people.
Somewhere in New Guinea, there most likely remain dozens of languages, cultures and tribal customs still unknown to modern man. But due to the largely uncharted terrain, and the unknown character of tribal inhabitants amid reports of cannibalism, rural New Guinea is seldom explored. While new tribes are discovered every so often, many expeditions that depart with the purpose of tracking them down are cut short—and sometimes they simply go missing. In 1961, for example, Michael Rockefeller set forth with the intention of finding some of the lost tribes. Rockefeller, an American heir to one of the largest fortunes in the world, was separated from his group and is thought to have been captured and eaten by tribesmen.
In 1984, an unknown group of Aborigines were encountered near a settlement in Western Australia. After fleeing, the Pintupi Nine, as they were later called, were tracked down by speakers of their own language and told that there existed a place where water flowed from pipes, and where there was a general surplus of food. While most of the group decided to stay in the modern town—a few of them becoming traditional artists—one member, Yari Yari, returned to the Gibson Desert, where he remains today.
The Sentinelese are a tribe of about 250 people who live on North Sentinel Island, between India and Thailand. We don’t know much more than that, because every time the Sentinelese receive a visitor, they greet him with a hail of arrows. A few peaceful encounters in the late 1960s gathered most of what we now know about their culture. Coconuts delivered to the beaches as a gift were eaten, rather than planted. Live pigs were shot with arrows, and then buried without being eaten. The most well-received items were red buckets, which were promptly taken away by the Sentinelese sentinels—though similar green buckets were left behind. Anyone trying to land on the islands today should write out his will first. A National Geographic team was forced to turn back after the lead team member got an arrow through his thigh, and two local guides were killed. The Sentinelese also have a reputation for being able to survive natural disasters—unlike many of the modern people who live in similar environments. For instance, these coast-dwelling people successfully escaped the effects of the 2004 Boxing Day Tsunami, which wreaked havoc in Sri Lanka and Indonesia. Evan V. Symon is a moderator at Cracked.com, whose work can be viewed here